Bond Price Par Value And Ytm Coupon Rate

Bond ytm calculator outputs.
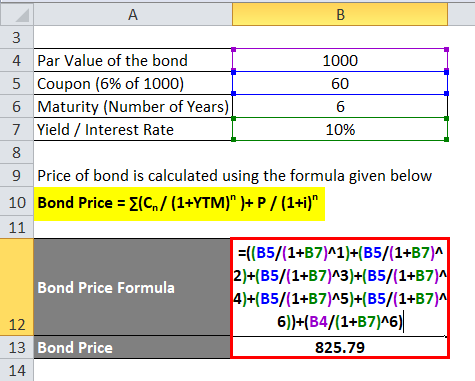
Bond price par value and ytm coupon rate. The formula for ytm is as follows. Current bond trading price the price the bond trades at today. Yield to maturity basis the yield to maturity ytm is the yield an investor can expect if holding the bond until maturity. In such a situation the yield to maturity is higher than the coupon.
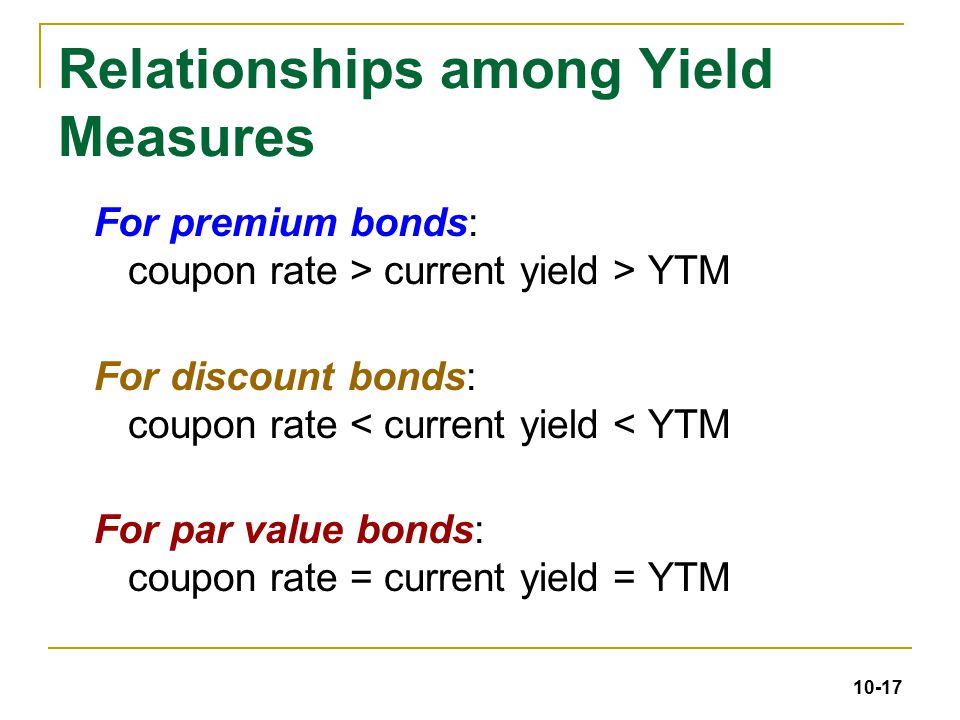
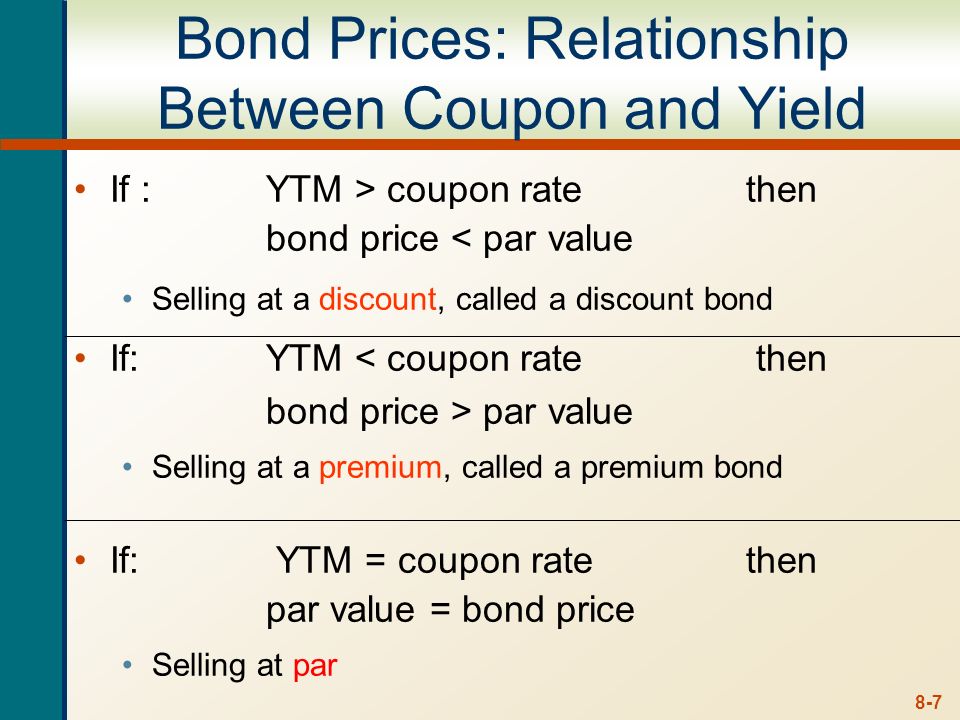
Let us assume a company abc ltd has issued a bond having the face value of 100 000 carrying a coupon rate of 8 to be paid semi annually and. The yield to maturity ytm is the percentage rate of return for a bond assuming that the investor holds the asset until its maturity date. The bond sells at a discount if its market price is below the par value. Therefore each bond will be priced at 1 041 58 and said to be traded at a premium bond price higher than par value because the coupon rate is higher than the ytm.
The yield to maturity only equals the coupon rate when the bond sells at face value. When the bond price is greater than the face value equal to the face value less than the face value the bond trades above par or at a premium at par below par or at a discount occurs when coupon rate is greater than ytm coupon rate is equal to ytm coupon rate is less than ytm issuers tend to trade bonds close to par. What is the coupon rate of a bond that makes semi annual coupon payments and has a current price of 967 70 a par value of 1000 a ytm of 8 2 and has 13 5 years until maturity. Yield to maturity calculator inputs.
Alternatively the causality of the relationship between yield to maturity cost of debt the cost of debt is the return that a company provides to its debtholders and creditors. The concept of pricing of this kind of bond is very important from the perspective of an investor because bonds are an indispensable part of the capital markets. A bond that sells at a premium where price is above par value will have a yield to maturity that is lower than the coupon rate. Yield to maturity.
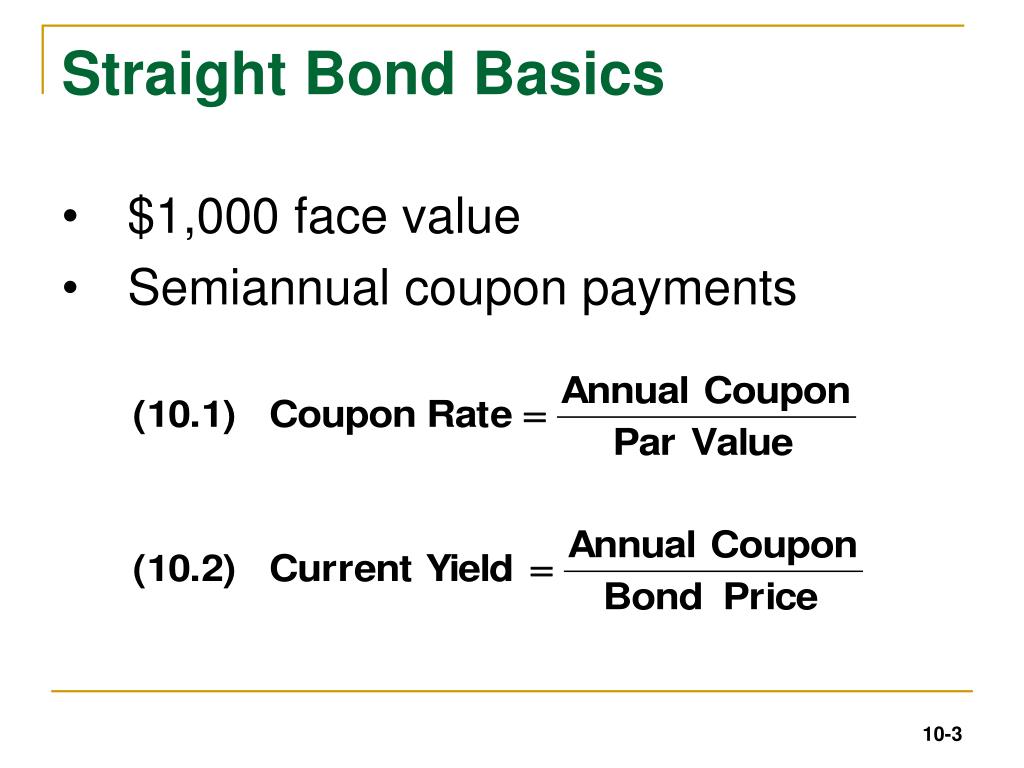
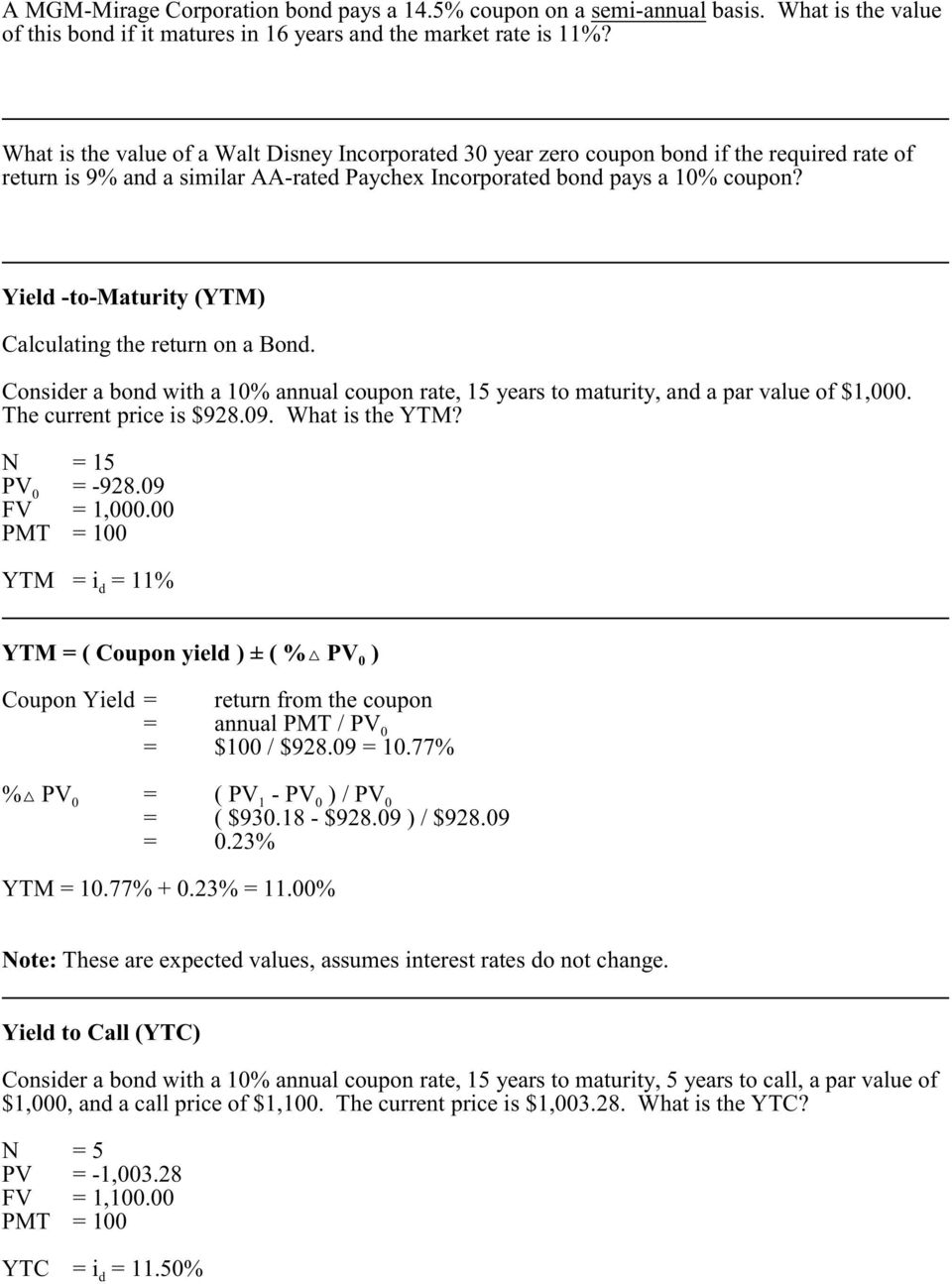
The converged upon solution for the yield to maturity of the current. This formula can be difficult to remember. It is the sum of all of its remaining coupon payments. Bond face value par value the face value of the bond also known as the par value of the bond.
Years to maturity the numbers of years until bond maturity. Let us take an example of a bond with semi annual coupon payments. Since the coupon rate is lower than the ytm the bond price is less than the face value and as such the bond is said to be traded at discount. Bond price 83 878 62.
So it will be 1 041 58. Market price fluctuates due to the bond getting closer to its maturity date. The par value of a bond is its face value or the stated value of the bond at the time of. If the price of the bond falls to 800 then the yield to maturity will change from 2 to 2 5 i e 20 800 2 5.