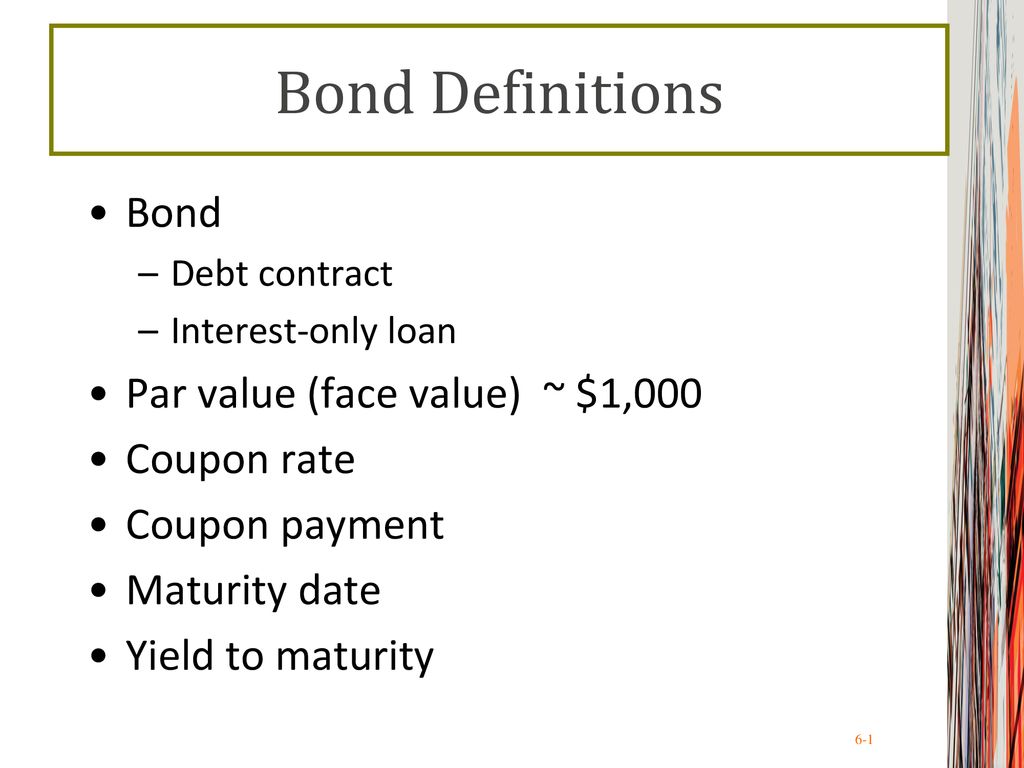
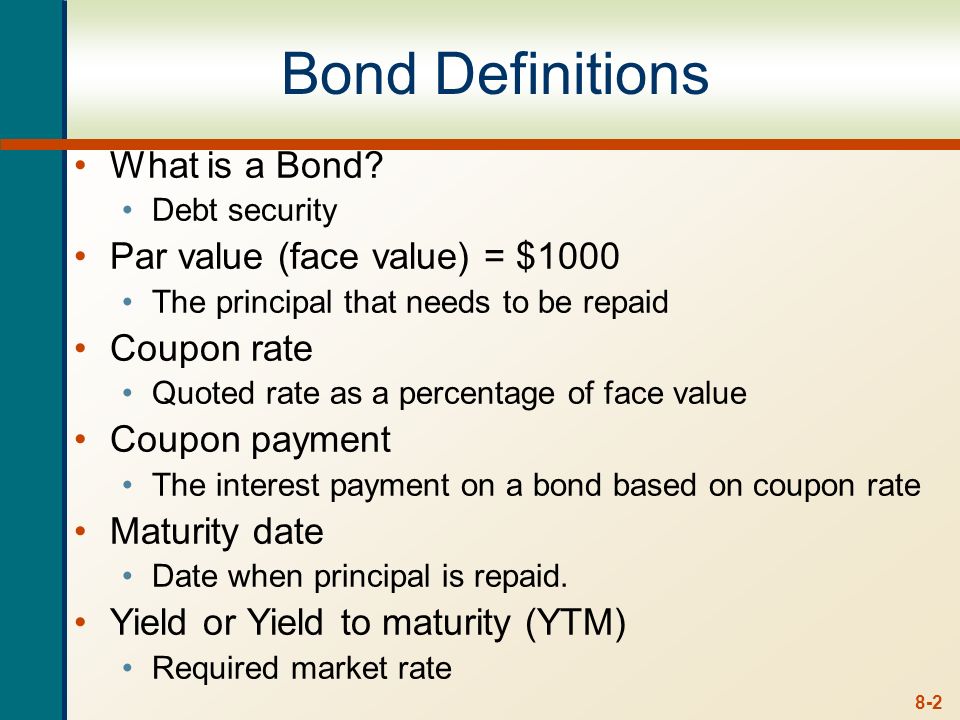
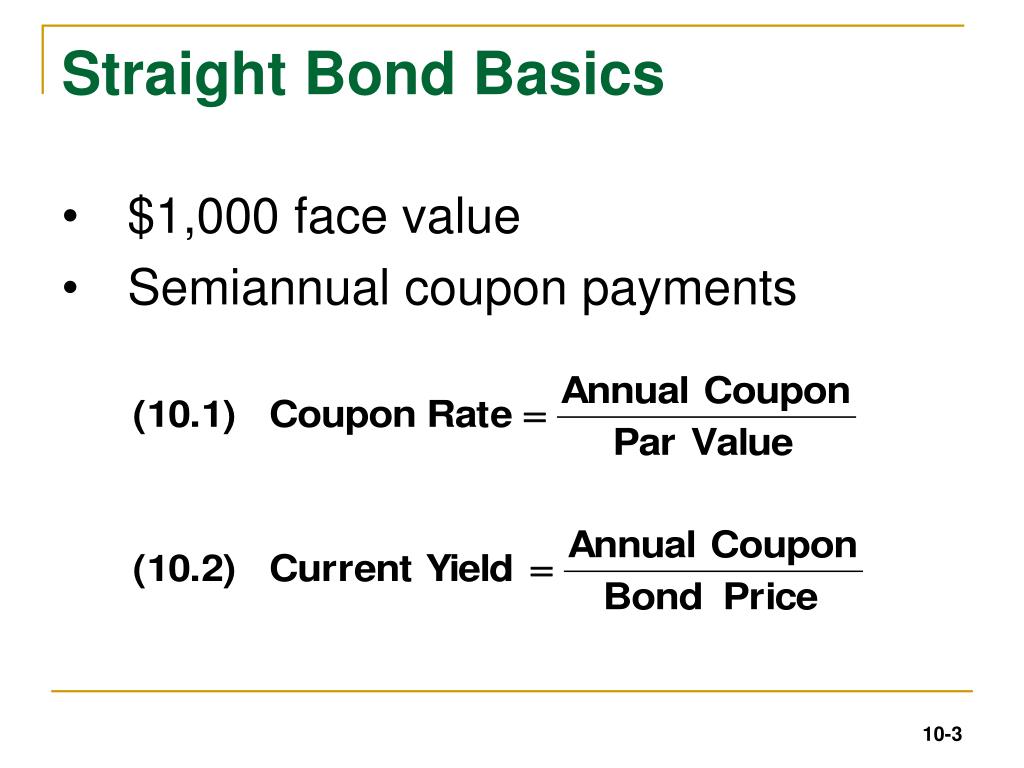
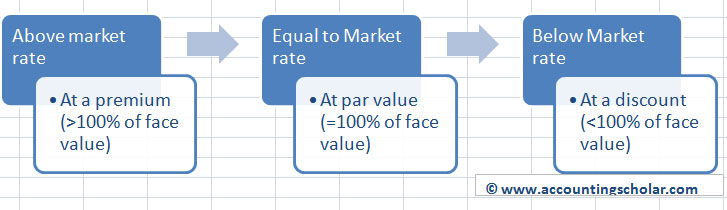
Par Value And Face Value
As bonds approach maturity actual value approaches face value.
Par value and face value. Face value synonyms face value pronunciation face value translation english dictionary definition of face value. Par value is the face value of a bond. Par value is the nominal or face value of a bond or stock or coupon as indicated on a bond or stock certificate. Face value also sometimes called par value is an accounting representation of the value of a company s common stock on it s balance sheet.
Par value also called the maturity value or face value. With stocks par value is a mostly arbitrary number. Par value vs face value. Apparent significance or value.
In the case of stock certificates face value is the par value of the stock. For example if a bond certificate says 1 000 the face value is 1000. Bonds pay the face value at maturity and calculate coupons as a percentage of the. Face value also known as par value is the value of a company listed in its books and share certificate.
Learn 100 online from anywhere in the world. The company decides the face value when it offers shares at the time of issuance. Par value and face value are most important with bonds as they represent how much a bond will be worth at the time of the bond s maturity. The face value of a share is fixed until the company decides to split or reverse split the shares.
The value printed or written on the face as of a coin or postage stamp. Initial offerings are made available at par value of the face value to make them look attractive after listing and the stocks mostly open at a rate higher than the face value bringing profits for the investor. Face value and par value are investment terms that are related to bonds and stocks. Here s a look at cipla s balance sheet the equity share capital shown is calculated as face value x no.
Par value is important for a bond or fixed income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments. Before maturity the actual value of a bond may be greater or less than face value depending on the interest rate payable and the perceived risk of default.