Par Value Definition Government
Par value stock is one class of stock issued by a corporation that has a par value set in the corporate charter or articles of incorporation.
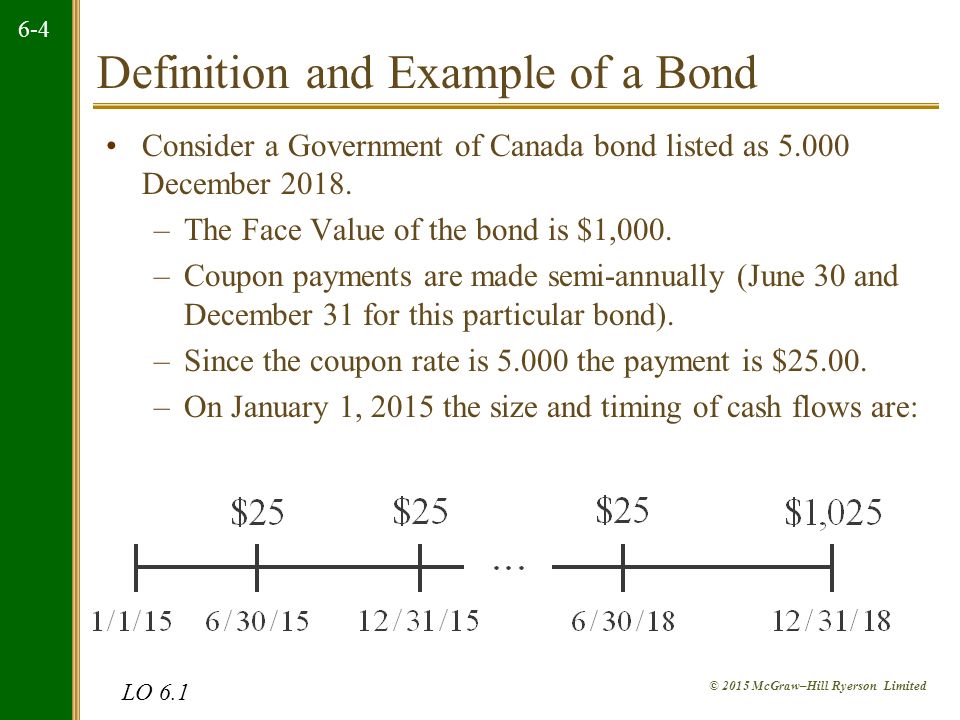
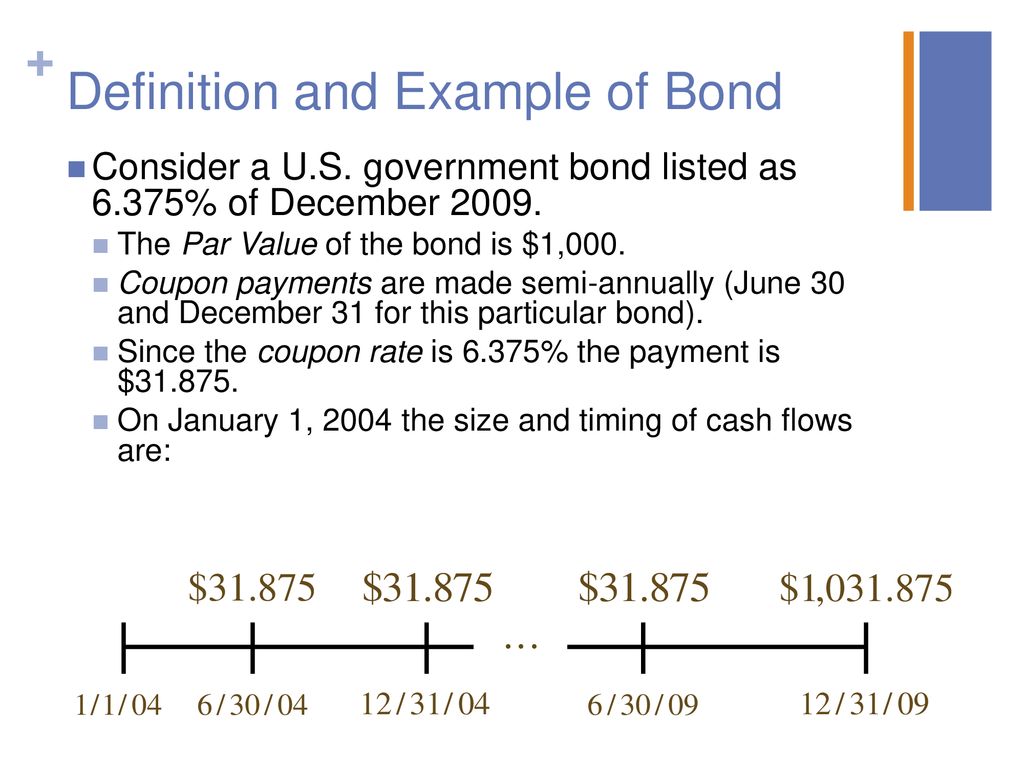
Par value definition government. Bond interest rates are quoted as a percentage of the par value of the bond. Par value is also called face value or nominal value it is the amount stipulated in the bond contract however par value does not include interest payments. For example if a bond certificate says 1 000 the face value is 1000. The par fund invests in a range of assets to generate an investment return.
Par value stock. Par value is important for a bond or fixed income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments. Par value of bonds definition. The par value is a minimum selling value given to each share of stock.
A bond selling at par is priced at 100 of face value. When a corporation is setup or incorporated a corporate charter is created. What does par value stock mean. It may do so by issuing 1 000 bonds each with a 1 000 par value.
How to use par in a sentence. The par value of bonds definition refers to the principal the amount of money the bondholder receives when the bond matures. The fund s assets can include government and corporate bonds equities properties and cash. Par value in finance and accounting means stated value or face value.
Par can also refer to a bond s original issue. From this come the expressions at par at the par value over par over par value and under par under par value. Let s assume company xyz issues 1 000 000 in bonds to the public. Par value is the face value of a bond.
Par value also called the maturity value or face value. Most corporate bonds have 1 000 face values but municipal bonds often have 5 000 par values and federal bonds often have 10 000 par values. When buying a par policy your premiums will be pooled together and invested with premiums from other policyholders in the fund. Par definition is the established value of the monetary unit of one country expressed in terms of the monetary unit of another country using the same metal as the standard of value.
The amount that an issuer agrees to pay at the maturity date. When each bond matures the borrower will pay back the par value of 1 000 to the lender.




/GettyImages-1058454392-146fd62a8b20476fa0888ecfa18868ae.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/thinkstockphotos_493208894-5bfc2b9746e0fb0051bde2b8.jpg)
/16c2bc813fac68e26f0f7aea199a1cc9-dfac742897bb40eea19f17122bebf07e.jpg)