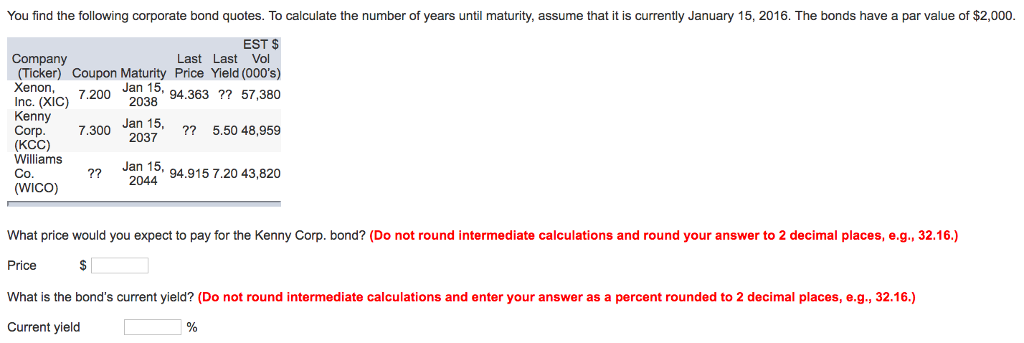
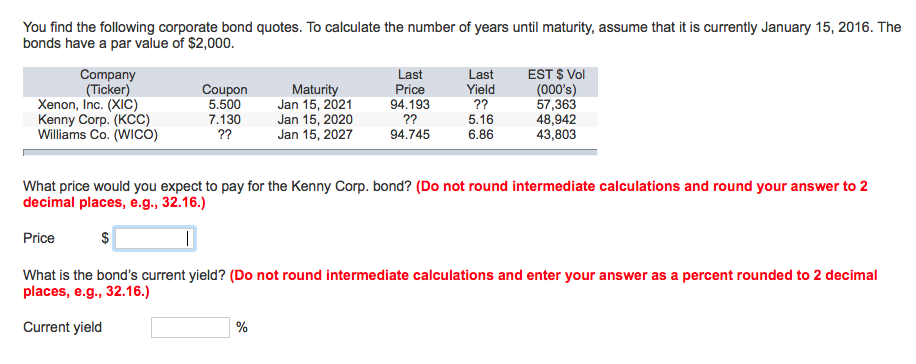
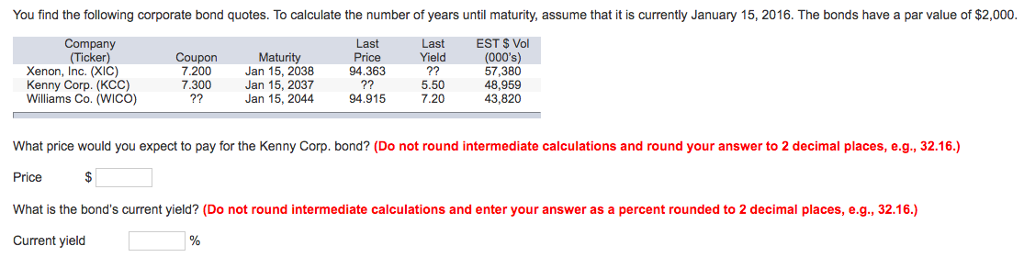
Par Value Of A Corporate Bond

Lastly the bond is a 10 year corporate bond and has two years before maturity.
Par value of a corporate bond. Face value is also known as par value. Example of a par bond. Par value is the face value of a bond. A bond with a face value of 100 and a maturity of three years comes with a coupon rate of 5 paid annually.
What is par value. This is the amount of money that bond issuers promise to be repaid bondholders at a future date. Suppose the corporate bond has a coupon rate of 5 percent and a face value of 1 000. The par value of stock has no relation to market value and as a concept is somewhat archaic.
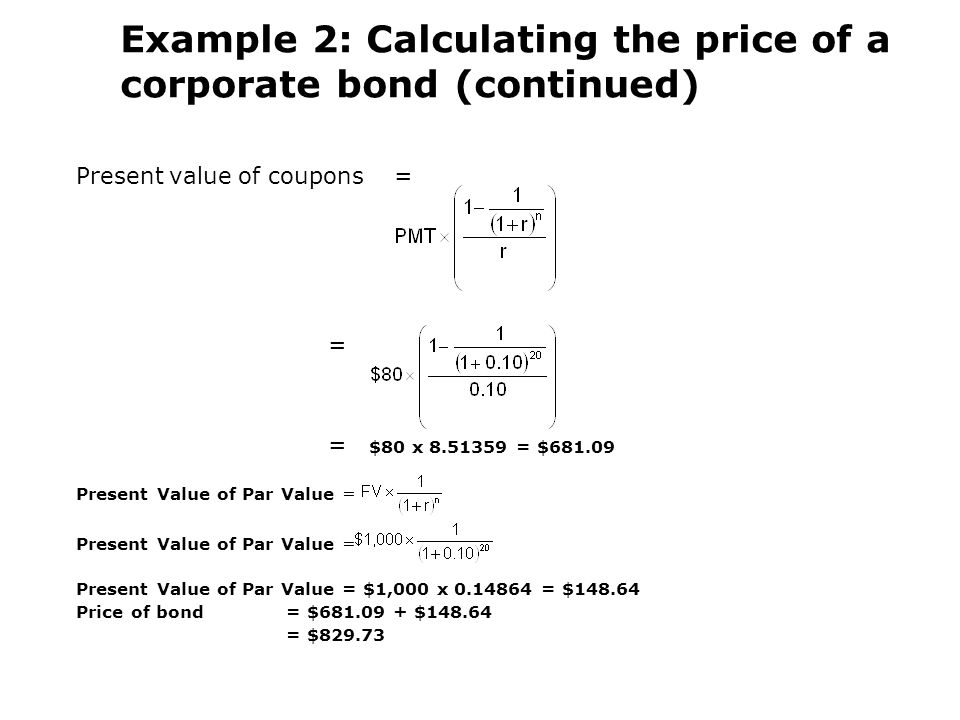
Using the bond pricing formula to mathematically confirm that the bond is priced at par. Par value is the nominal or face value of a bond share of stock or coupon as indicated on a bond or stock certificate. For instance a company might issue 500 15 year bonds to the public. The par value of a bond also called the face amount or face value is the value written on the front of the bond.
The certificate is issued by the lender and given to a borrower or by a corporate issuer and given to an investor. Also assume that the bond pays out interest once a year and thus the annual coupon payment is 1 000 x 5 percent 50. Par can also refer to a bond s original issue value or its value upon redemption at maturity.




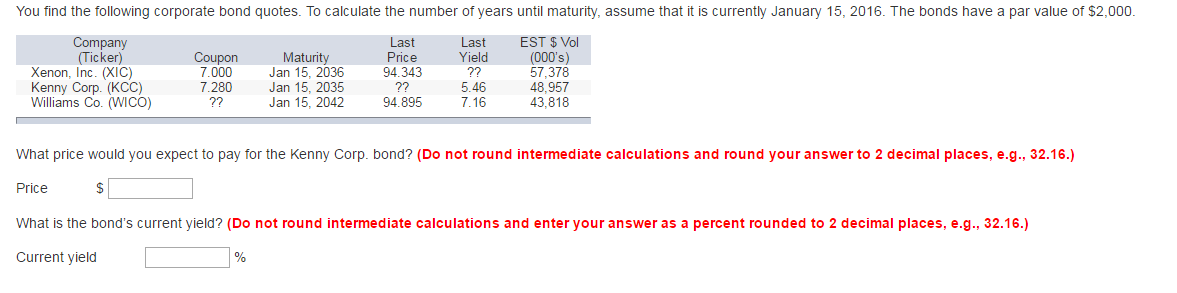




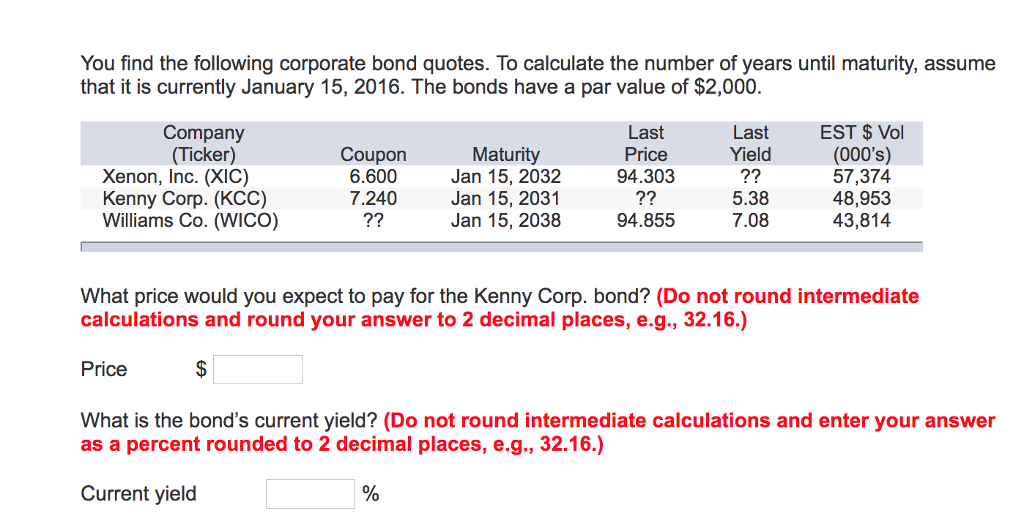


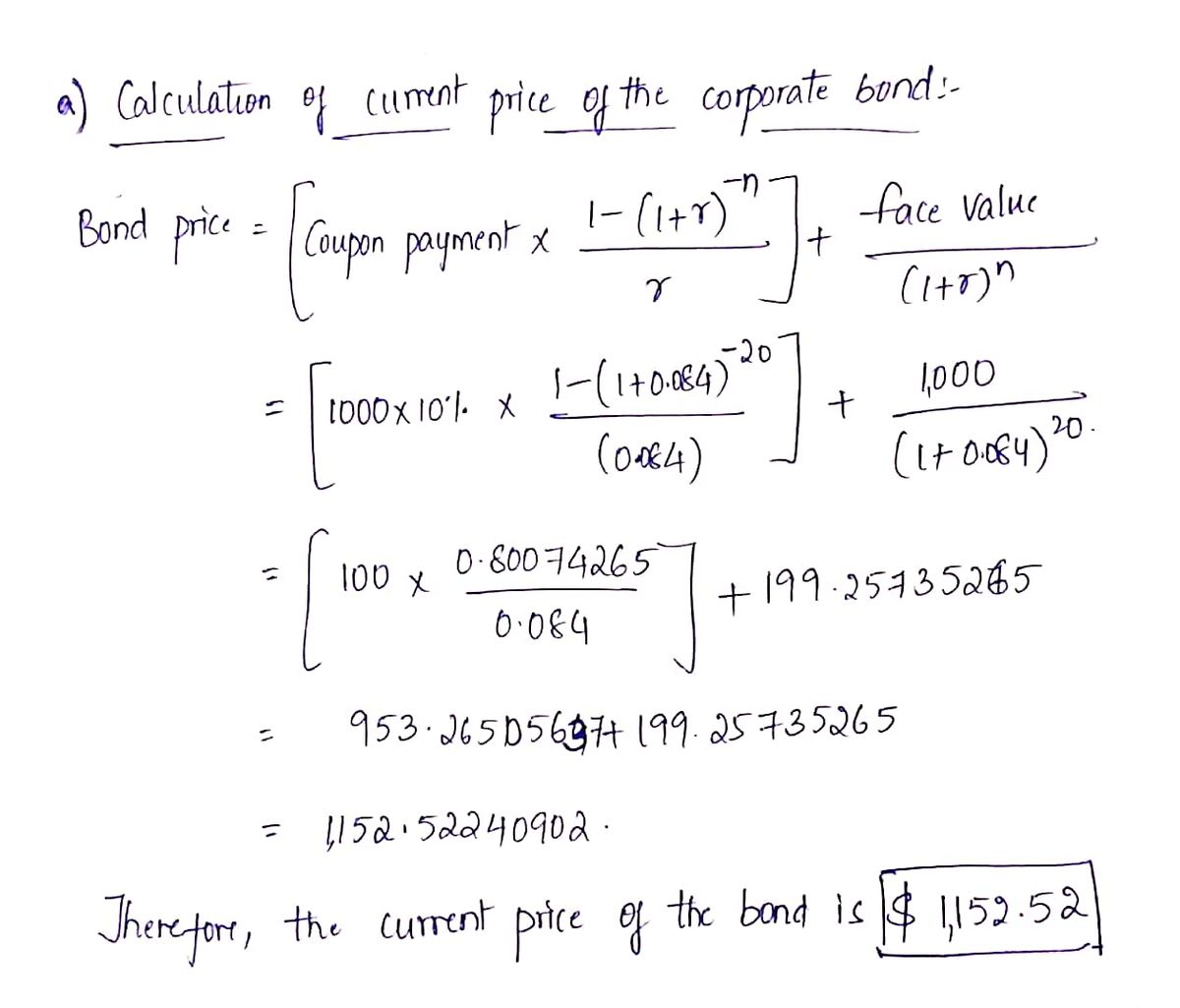
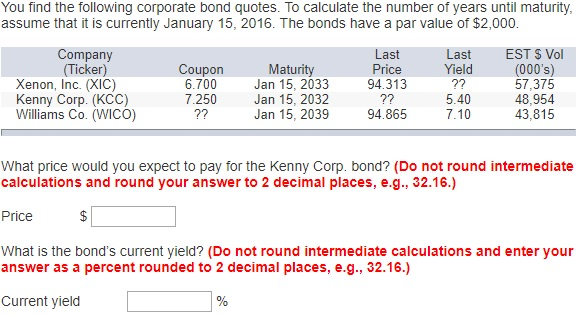
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CorporateBonds_CreditRisk22-8c12f1dbc1494f28b3629d456fb4fa63.png)