The Par Value Of Ordinary Shares Represents

The amount that an issuer agrees to pay at the maturity date.
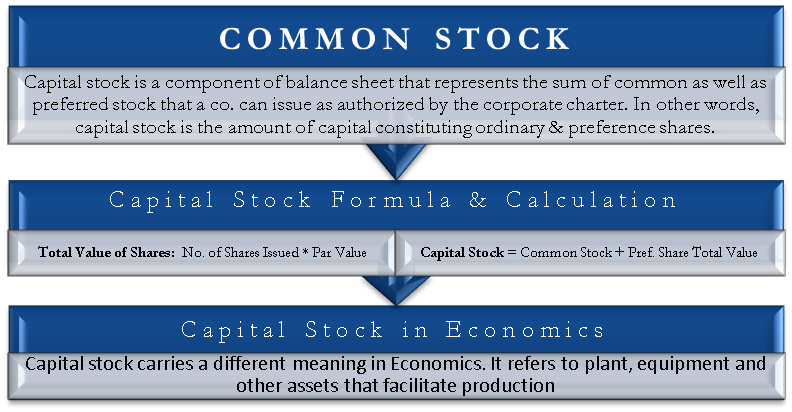
The par value of ordinary shares represents. The northern company issued 100 000 shares of its 1 par value common stock and 25 000 shares of its 100 par value preferred stock. So multiply the number of shares issued by the par value per share to calculate the par value of preferred stock. Make journal entries to record these transactions in the books of northern company if the shares are issued. Holders of ordinary shares are typically entitled to one vote per share and do not have any.
Face value the amount of money stated on a bond or rarely a stock certificate. Par value of preferred stock number of issued shares x par value per share. The call price is usually either par value or a small fixed percentage over par value. The amount received by the corporation when the share was originally issued 71 when shares are sold at an amount higher than par value the excess over par shall be credited to 72 any direct costs incurred to issue shares.
There is a theoretical liability by a company to its shareholders if the market price of its stock falls below the par value for the difference between the market price of the stock and the. The legal nominal value assigned to the share d. The par value is unrelated to the price at which the shares are first issued or their market. All you have to do now is run a simple calculation.
The par value of a common share is an arbitrary value assigned to shares to fulfill state requirements. Par value for stock. In this example multiply 1 000 by 1 to get 1 000 in par value of preferred stock. The book value of the share b.
Par value is the stock price stated in a corporation s charter. The intent behind the par value concept was that prospective investors could be assured that an issuing company would not issue shares at a price below the par value. The shares in a corporation may be issued partly paid which renders the owner of those shares liability to the corporation for any calls on those shares up to the par value of the shares. The liquidation value of the share c.
Par value also called the maturity value or face value. 70 the par value of an ordinary share represents a. Also par value still matters for a callable common stock. For example if a bond certificate says 1 000 the face value is 1000.
Bonds pay the face value at maturity and calculate coupons as a percentage of the. Ordinary shares a synonym of common shares represent the basic voting shares of a corporation.