What Is Meant By Par Value Of Shares

Par value is important for a bond or fixed income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments.
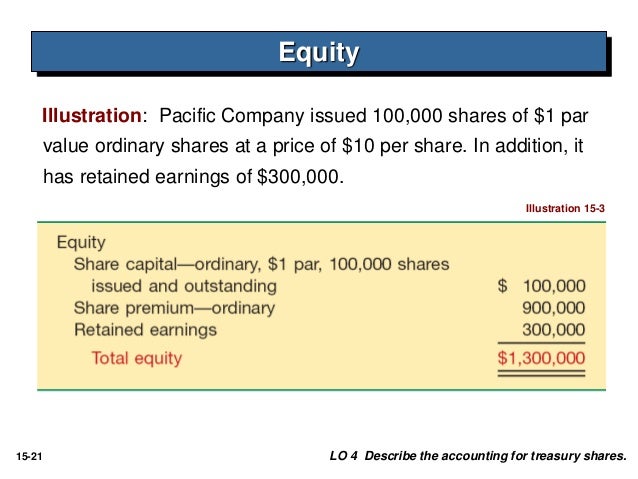
What is meant by par value of shares. In general par value also known as par nominal value or face value refers to the amount at which a security is issued or can be redeemed for example a bond with a par value of 1 000 can be. The call price is usually either par value or a small fixed percentage over par value. The objectives of its issuance include 1 avoidance of taxes levied according to the share s face value 2 avoidance of the issuer firm s liability to shareholders in the event the shares have to. The shares in a corporation may be issued partly paid which renders the owner of those shares liability to the corporation for any calls on those shares up to the par value of the shares.
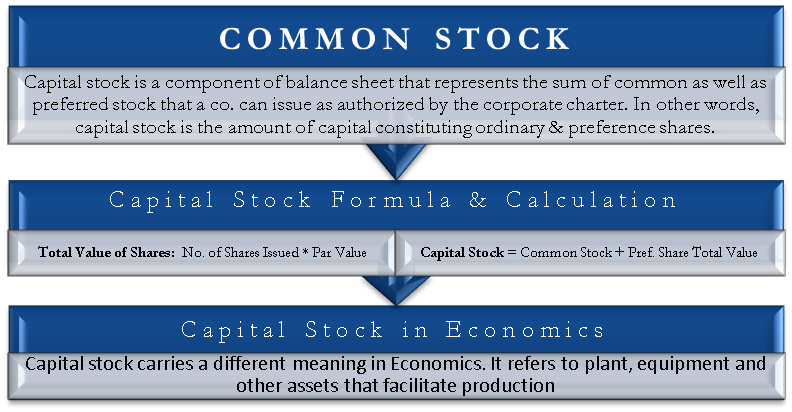
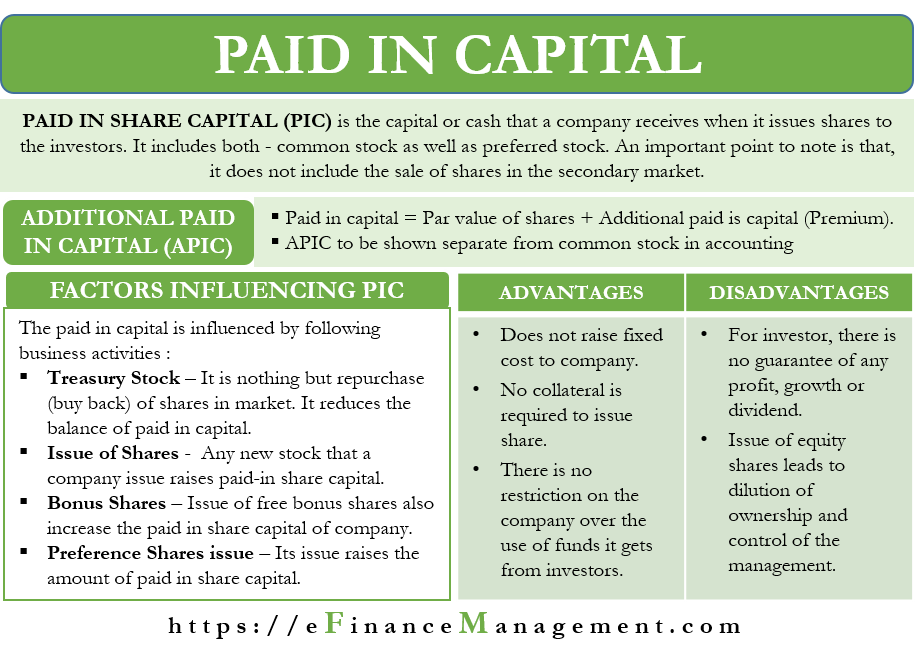
This will be shown as a separate amount in the paid in capital or contributed capital section of. A company can change the par value of its shares by a reorganization or share split for example issuing four 25p par value shares for every 1 share held. Also par value still matters for a callable common stock. No par value npv share.
Par value is the face value of a bond. Par value of shares also known as the stated value per share is the minimal shares value as decided by the company which is issuing such shares to the public and the companies then will not sell such type of shares to the public below the decided value. What is par value of share. When a corporation s common or preferred stock has a par value corporation s balance sheet will report the total par value of the shares issued for each class of stock.
There is a theoretical liability by a company to its shareholders if the market price of its stock falls below the par value for the difference between the market price of the stock and the. In other words it is the share nominal amount 1 0 1 or 0 001 mentioned on the stock certificate at the time. The par value of a share bears little relationship to its market value which is determined by demand and supply for the shares.