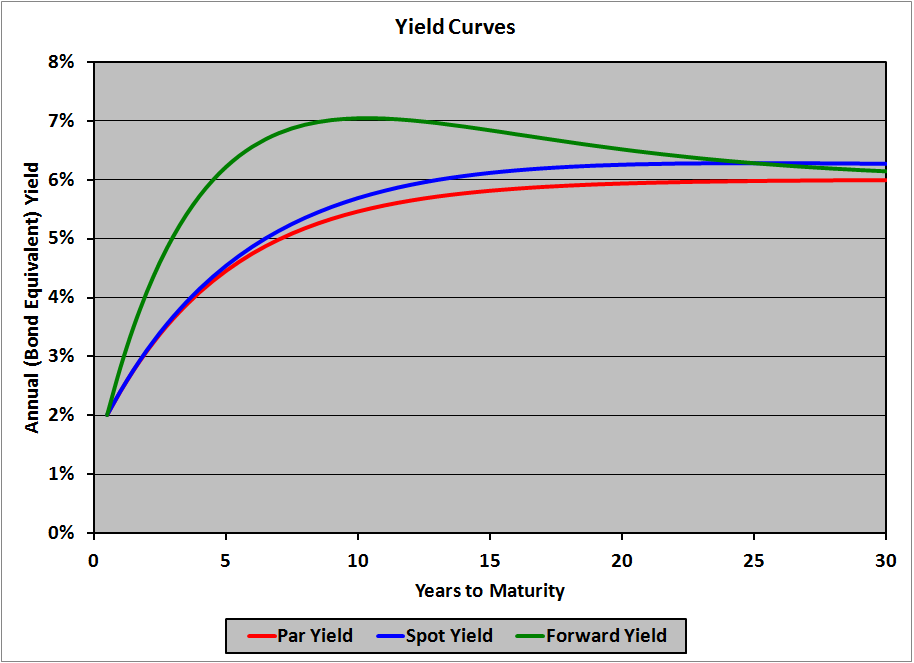
Par Yield Curve Spot Rate Curve

The par curve differes from the spot curve in that it is a sequence of yields to maturity such that each bond is priced at par value.
Par yield curve spot rate curve. Given below is the step by step process to arrive at the spot curve using the bootstrapping method. The par curve is obtained from the spot curve. When people quote the par curve. The spot rate treasury curve can be used as a benchmark for.
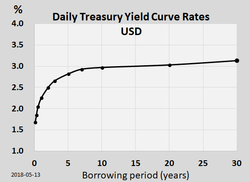
Priced in the market at par. The par yield curve can be derived directly from bond yields when bonds are trading at or near par. Trying to keep the math out of the answer a par curve is the most commonly referred to curve by media and market watchers. Spot rate treasury curve.
To me the hard part is the definition of par yield the par yield is the yield to maturity that prices a bond exactly at par so this is about the relationship between yield and the spot rate curve. If bonds in the market are trading substantially away from par then the resulting curve will be distorted. On the par yield curve the coupon rate will equal the yield to maturity of the. It gives the ytm for zero coupon as opposed to coupon paying bonds.
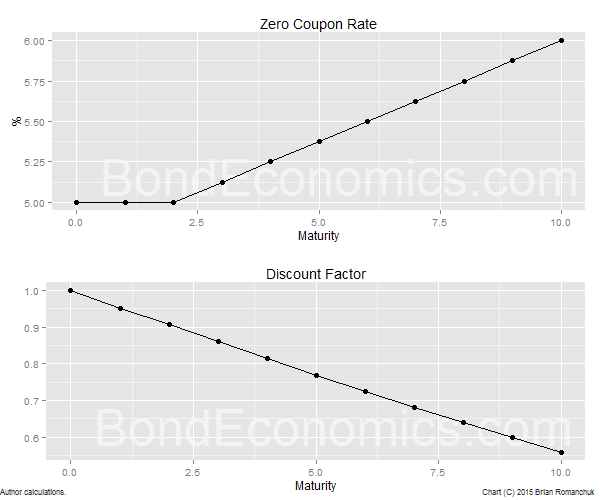
All bonds on the par curve are supposed to have the same credit risk periodicity currency liquidity tax status and annual yields. That s why a yield curve constructed in this way is also called a coupon curve. It is then necessary to derive it by iteration from the spot yield curve. In the bootstrapping technique one repetitively applies a no arbitrage implied forward rate equation to yields on the estimated treasury par yield curve.
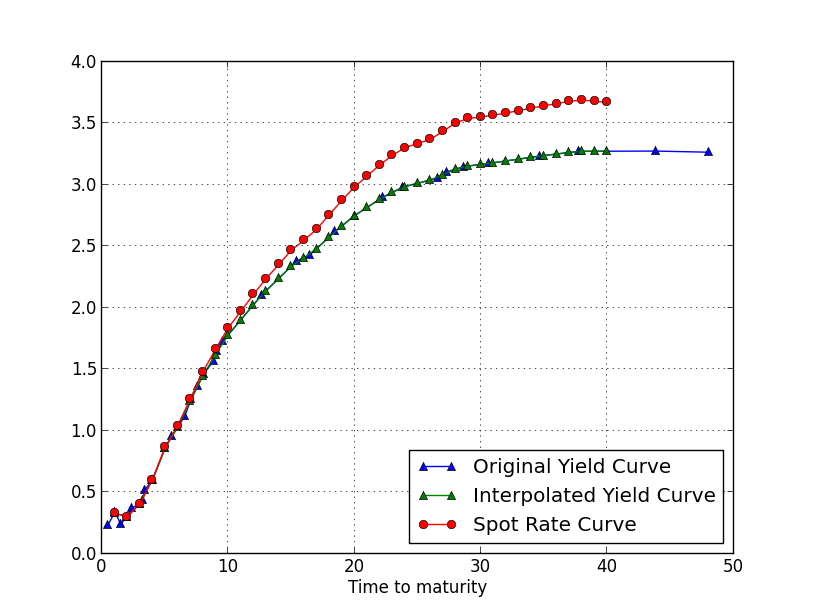
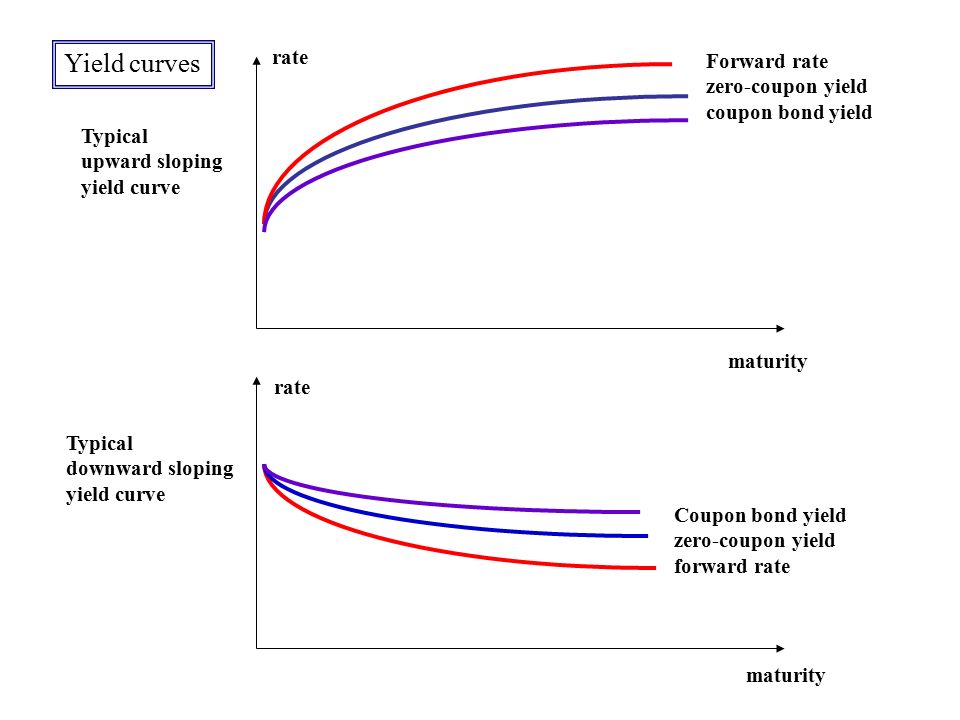
The spot curve is more often user to calculate the fair value of a particular bond. It is a construction of time to maturity at the x axis and yield to maturity on the y axis. The zero coupon or spot yield curve. Whereas the par curve gives a yield that is used to discount multiple cash flows i e all of the cash flows coupons and principal for a coupon paying bond the spot curve gives a yield that is used to discount a single cash flow at a given maturity called a spot payment.
The spot rate treasury curve is a yield curve constructed using treasury spot rates rather than yields. As explained for example here a bond that has theoretical coupons equal to its yield is priced at par 100. They are used to a determine the no arbitrage value of a bond b determine the implied forward interest rates through the process called bootstrapping and c plot the yield curve. In this video the spot rate curve is upward sloping such that the 4 year zero rate is 9 00 and the implied 4 year par yield is 8 57.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Par_Yield_Curve_Apr_2020-01-3d27bef7ca0c4320ae2a5699fb798f47.jpg)
/dotdash_Final_Par_Yield_Curve_Apr_2020-01-3d27bef7ca0c4320ae2a5699fb798f47.jpg)


/dotdash_Final_Par_Yield_Curve_Apr_2020-01-3d27bef7ca0c4320ae2a5699fb798f47.jpg)